Corneal Collagen Crosslinking (CXL) is a technique that uses ultraviolet (UV) light and a photosensitizer called riboflavin (liquid vitamin B2) to strengthen the cornea and attempt to reduce the progression of Keratoconus (KCN) or post-LASIK ectasia.
A healthy cornea is shaped like a basketball (spherical), while patients with Keratoconus or corneal ectasia have irregularly shaped corneas, appearing more like the pointed end of a football. When the thin cornea bulges outward, it leads to impaired vision.
Keratoconus is progressive, meaning there is a high chance it will continue to worsen with time. Crosslinking of collagen refers to the ability of collagen fibers to form strong bonds with other fibers. Collagen crosslinking occurs naturally with aging, which may be one reason why keratoconus progression is thought to slow with age.
As the disease progresses, continued thinning and scarring take place, creating a need for a corneal transplant for the patient to be able to see well. Crosslinking allows our doctors to treat the disease early, before scarring takes place, and reduce or eliminate the need for a transplant entirely.
During the Crosslinking procedure, the patient is first given numbing drops in their eye. A lid separator may be used to hold the eyelids open. Depending on the patient, the epithelial surface cells may be removed. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) drops are used to moisten the cornea until the riboflavin can be seen throughout the eye. This usually takes 15 to 30 minutes.
After the riboflavin is present throughout the cornea, the UV light is applied. The UV light portion of the treatment typically lasts about 30 minutes. Various drops and medications are prescribed to assist with the healing process.
A soft bandage contact lens may be placed over the cornea to aid in the healing, protecting the vulnerable cornea from wind and dust.
The patient is evaluated over the next several months (and beyond) to monitor the healing response and watch for keratoconus stability.
Following the procedure, eyeglasses or contact lenses may not work as well as they used to because crosslinking may change the prescription. It typically takes 4-6 weeks after the procedure before contact lenses or glasses prescriptions can be prescribed.
Below is a patient of ours showing how simple the procedure can be!
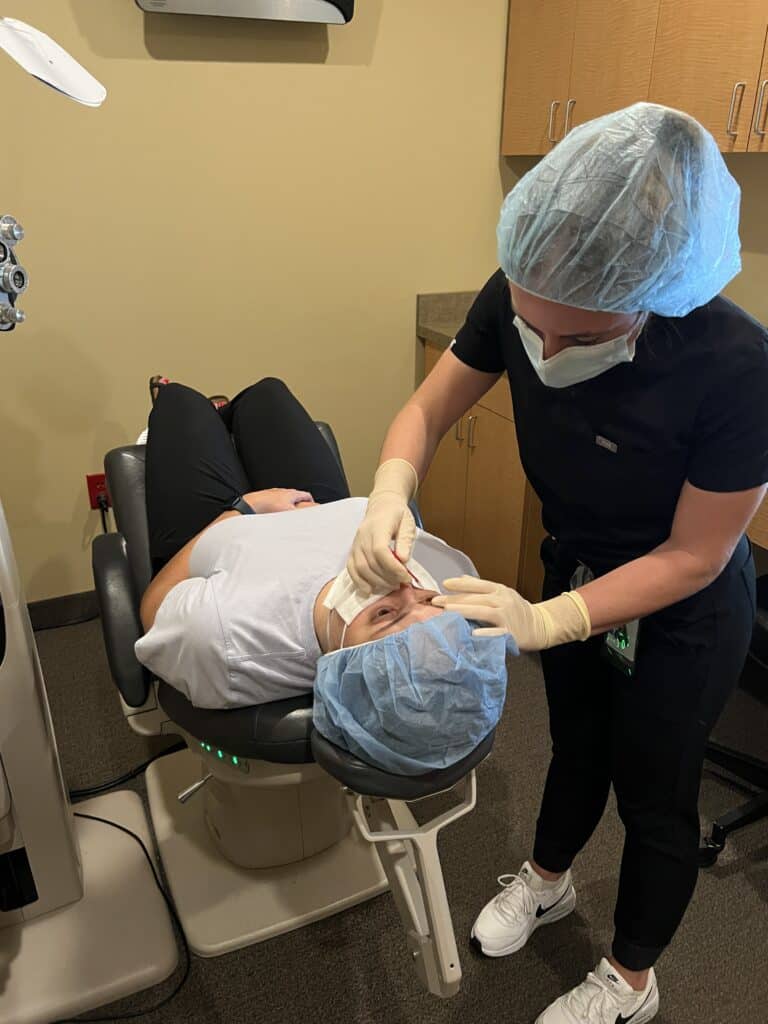
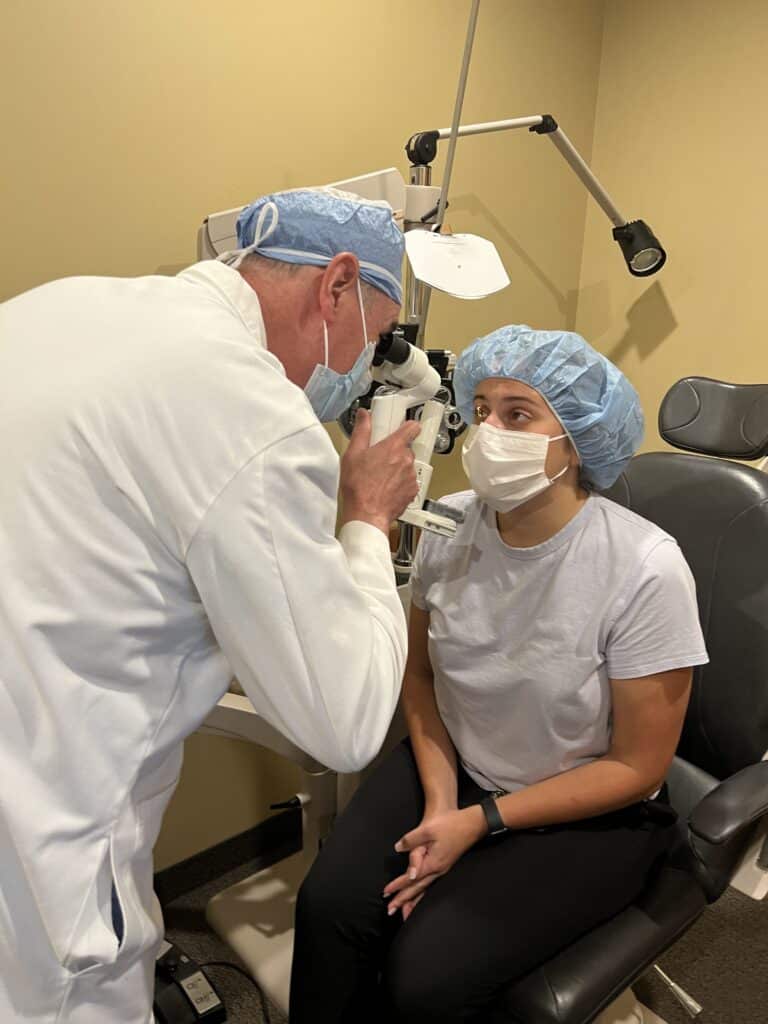
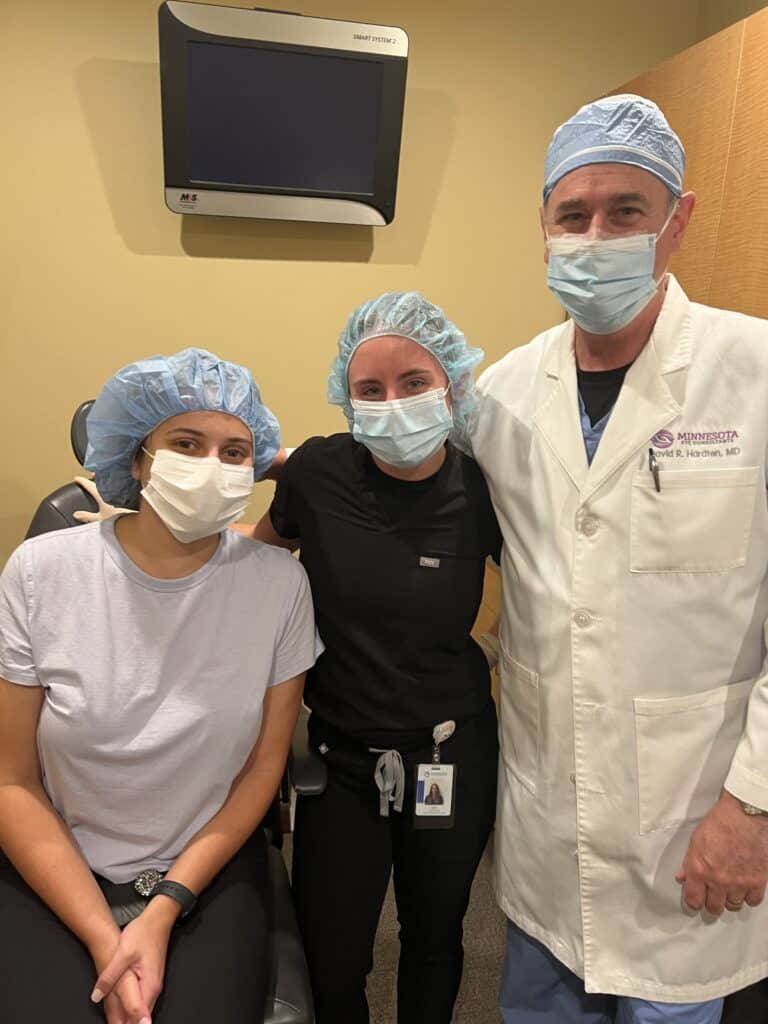
Epithelium-Off crosslinking was recently FDA-approved in the United States. Minnesota Eye Consultants offers both Full Epithelium-Off Crosslinking, as well as a variation called Partial Epithelium-Off. Please discuss with your surgeon the benefits and risks of each procedure.
Minnesota Eye Consultants is proud to offer patients convenient access to eye care across the Twin Cities. We have 5 locations, each with an onsite ambulatory surgery center (ASC).